What are the top three main goals you have for your website?
- You want users to find your website when they browse within Google’s search engine.
- You want them to trust your site and business enough, so they click your link to explore
- You want them to read your content, be impressed by what you have to say, and then take action.
Something like that, correct?
SEO is the key to turning these goals and expectations into a reality. However, many times, people aren’t aware that SEO is a lot about more than just using the right keywords on a page.
Technical SEO, which we’re going to look at today, is a critical piece of your website’s success in search. So, let’s unpack what exactly it is, why you need it, and start integrating it within your new or existing website.
Keep in mind; without a technical SEO on your staff, your website will never see the light of day!
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical Search engine optimization is a process used to help a website get to the top of relevant search results. When someone searches for something like “how do I manage my budget” or “kids clothing stores near me,” your website must be the one that appears on the first page of the search engine results page (SERPs).
But it’s no simple task, and without the technical SEO piece filled in, your website’s SEO strategy will be incomplete, and it’ll be tough to get to that much-coveted first SERP.
But that doesn’t explain what technical SEO is or how it plays its part. Here is a description of technical SEO:
Technical SEO involves optimizing your code, your rules, and all the surrounding elements that affect the way a website performs and how easily Googlebots can crawl your content.
Let’s look at this from two different but critical perspectives.
Your Visitors’ Point of View
What is it that makes people want to visit a website in the first place? Typically, it’s the promise of something. A product they need or a service promising to help them out of a bind. Even content that will teach them a skill they need to learn, etcetera.
We let prospects know they’ll find what they need with our website by positioning ourselves the right way in Google search.
This is a critical first step in the relationship between your business and potential clients.
That said, what happens when they finally land on your website? In other words, what is it that makes people want to stay on a website, read more, buy something, reach out to the company, and so on?
Having high-quality content and an attractive web design is a must. But if your technical SEO is not in order, bots and users will never see your on-page content/website.
Code Web will make sure your website loads fast, provides secure browsing and shopping experiences and is otherwise user-friendly.
Google’s Point of View
Although Google does have humans that review web pages to assess things like quality, authority, trustworthiness, and so on, it deploys bots to crawl the billions of online pages.
As you can imagine, robots can’t read a web page the way humans can. So, it’s not like they’re going to crawl your homepage and think, This is the perfect “coaching service” to show business owners.
Instead, bots focus on the signals the webpage sends, while humans concentrate on making sure webmasters are following Google’s best web design & SEO best practices, and there are 2 words for that! Manual Action.
This is why well-written code is so important. It’s also why things like security, speed, and mobile-friendliness, are accounted for when a web page is evaluated for rankability.
It’s not that Google is concerned with the machinery and code that makes a website function. What it’s focused on is identifying websites that perform well. That’s because there’s a direct correlation between technical performance and more satisfied visitors.
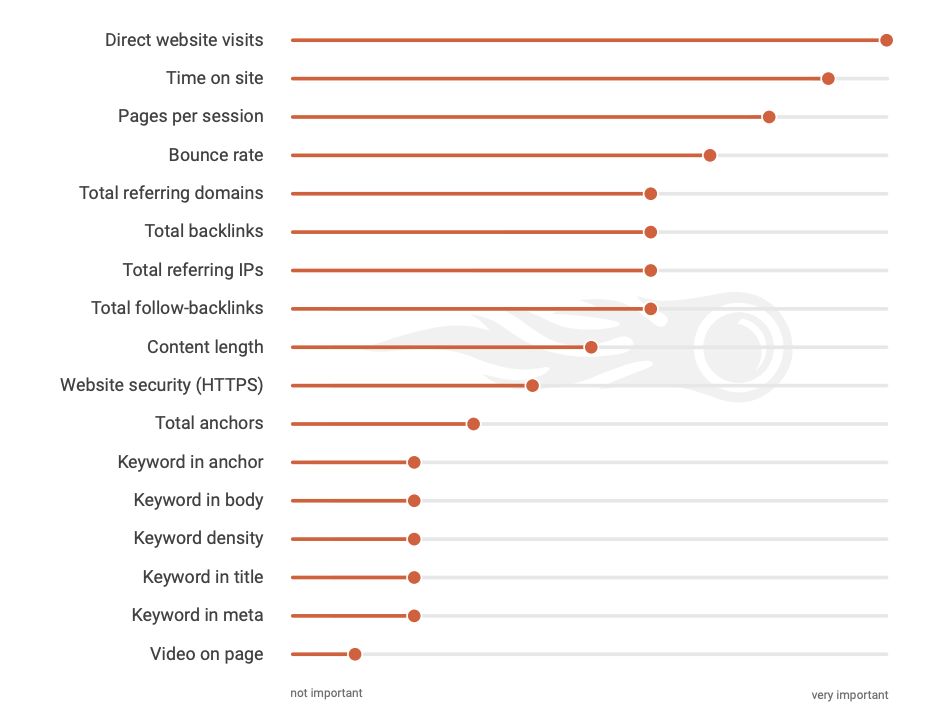
A recent study by SEMrush shows us how this plays out. According to the report, these are Google’s top-ranking factors:
Now, imagine your website was prolonged. How well do you think it would do in terms of factors like time on site, pages per session, and bounce rate? If it’s slow enough (and people’s threshold is only about three seconds these days), your site could be losing visitors almost immediately after acquiring them from search. Also, it takes a short time for a human mind to know if they will trust the website in question.
As Google begins to pick up on this trend, it’ll slowly but surely move your website deeper and deeper down in search results unless you audit your website with the best tools available, then fix all the issues.
Bottom line: If you don’t take care of the technical SEO factors that affect your visitors’ on-site experience, don’t expect visitors or Google to respond well to it and do you any favours.
Your Technical SEO Checklist
While a website should be built from the get-go with technical SEO in mind, a lot of this work requires ongoing maintenance (just like regular SEO). So, while the tips below may explain each optimization’s purpose as if it’s already in place, you can use this technical SEO checklist when first building-out your website.
Let’s take a look at what’s involved.
Optimize Your Web Hosting Plan
Because your web host is responsible for managing the server that provides the home-base for your website, you can’t afford to leave it in the hands of someone who doesn’t take things like security, speed, uptime, or SEO seriously.
So, that’s step #1: Make sure your web hosting company is reliable and reputable. If your web host can’t handle the underlying technology properly, then it won’t matter how much of the technical SEO work you do from this list.
You’ll learn rather quickly if the web hosting company you’re using is right for you. What you’ll have to keep your eyes on, though, is your web hosting plan. As your business and website grow, it’s not uncommon to outgrow your hosting plan. And that’s a good thing.
Step #2 will require you to assess how well your hosting plan is serving you.
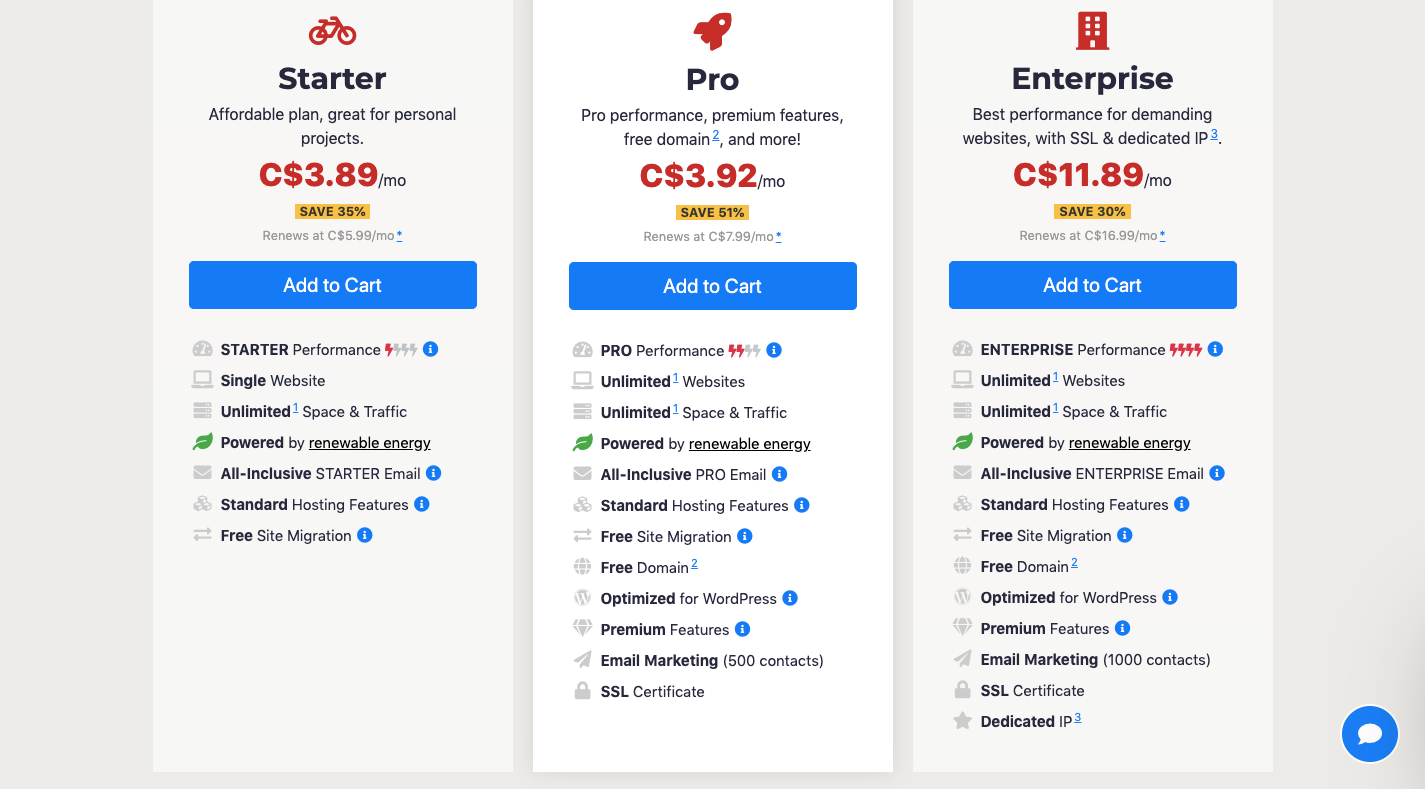
Let’s say you currently use Web Hosting Canada’s Starter plan.
You visit the list of their hosting plans — from the website or your hosting account — and make a side-by-side comparison of the plans.
The Starter plan was beneficial when your site was new, and you only had about 100 people visiting your website every day. And while there are no limits on space or traffic, there are other features you think would improve your visitors’ experience even further.
For instance, PRO and ENTERPRISE Performance would significantly speed up your loading times now that there are thousands of people trying to access your site every day. The WordPress optimization features would also help with that.
Plus, premium features like one-click restores and the SSL certificate are something you need to keep the increased traffic from spambots and hackers away.
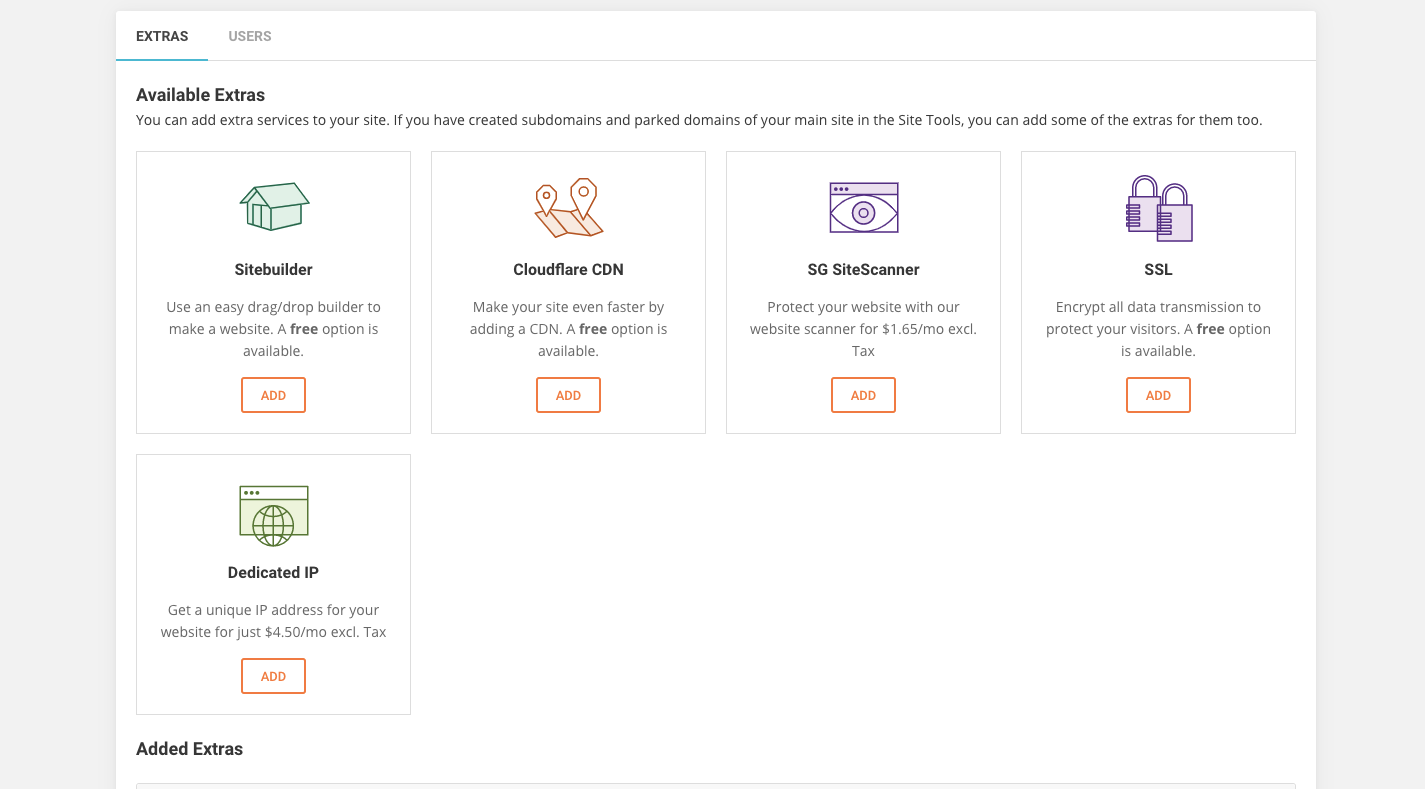
You can also look around your hosting control panel to see if there are other performance upgrades available.
A content delivery network (CDN) would make your site both faster and more secure. An SSL certificate isn’t just a must for security, but for SEO — it’s something Google pays attention to when ranking a site (more on that next). And a SiteScanner tool would be useful for monitoring for security threats.
These are just examples of the kinds of features your web host might offer. You may also discover tools that speed up your site or help with SEO. So, take some time to explore and see what you can do to upgrade not just your plan but your SEO strategy.
Move to HTTPS
An SSL certificate is a security feature that adds encryption to a website. When installed, it moves your website away from this:
http://yourdomainname.com
To this:
https://yourdomainname.com
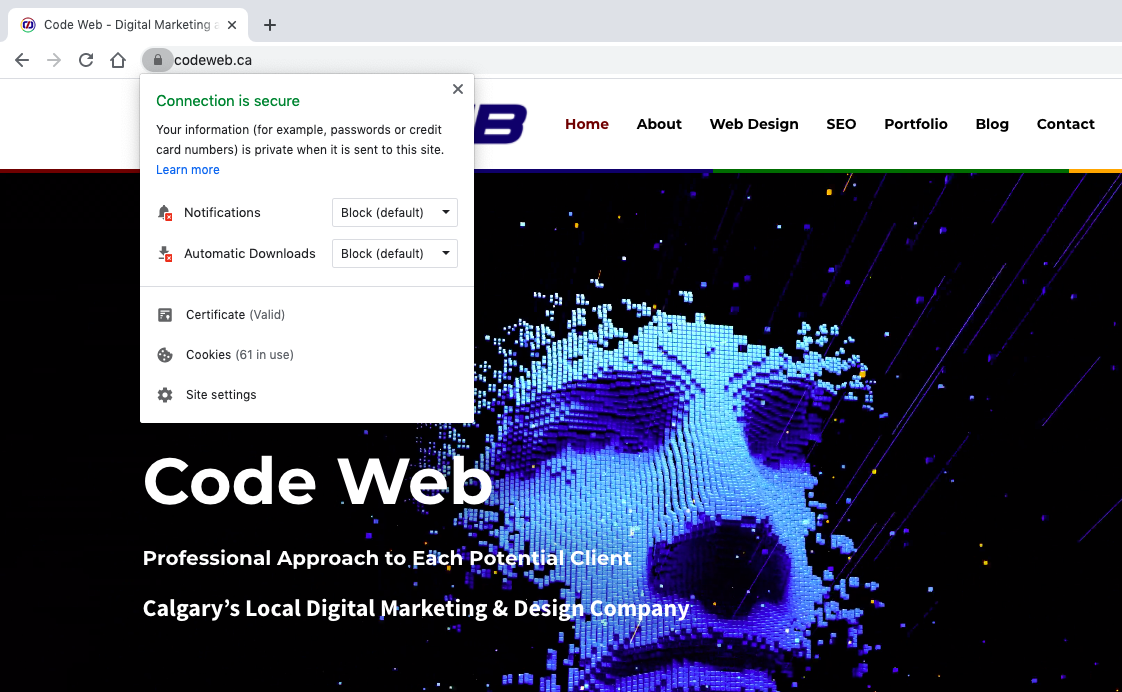
Not only that, but it displays a security notice to visitors in the browser address bar. It looks something like this:
When you’re accepting any information from visitors — be it as simple as their email address or more sensitive like their credit card information — you want to keep it hidden from hackers’ eyes. And that’s what this encryption helps with.
Ideally, your website has an SSL certificate starting on Day 1. If it doesn’t, then it’s something you 100% need to have installed as soon as you can.
As we’ve seen with Web Hosting Canada examples, you can easily add this layer of security to your site from your web hosting control panel. If your current hosting company doesn’t offer one, you can get a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt.
We have all seen & heard “Get an SSL Certificate” a million times within the past few years, but it’s that important! Code Web builds on HTTPS from the get-go 100% of the time. It is crucial.
Make Your URLs User-friendly
Remember how I mentioned that it’s both visitors and Google that you have to please? Well, this is one of those things where Google is going to care a lot more about it than your visitors (though some of them may take notice, too).
Here’s what I mean when I talk about user-friendly URLs:
Let’s say you run an accounting business, and your blog’s content is all about money management. Your post URLs might look like this if you rely on your site’s default URL structure settings:
https://yourdomainname.com/blog/07/20/how-to-get-your-budget-under-control-in-30-days-time-and-watch-your-profits-grow/
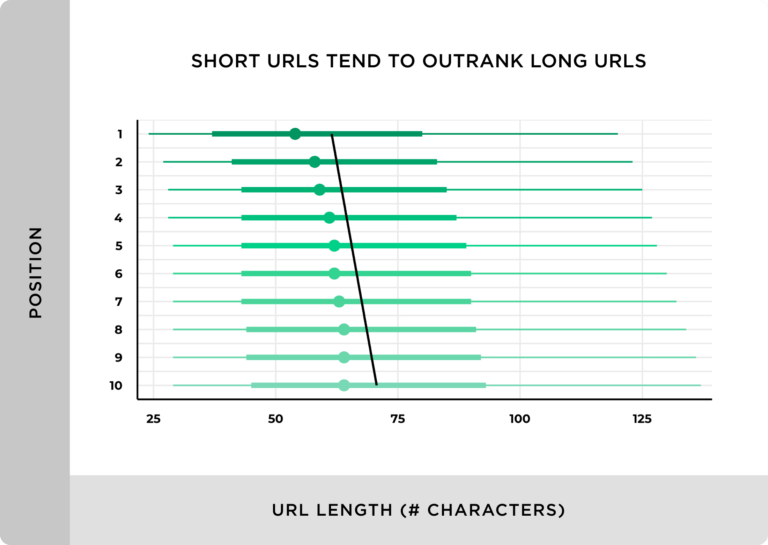
On average, URLs in the top spots in Google have about 66 characters. The example from above has 119.
But it’s not merely about length. It’s about clarity and context. Your URL needs to tell Google and visitors as succinctly as possible what the page is about. So, a way to improve this would be to remove the date (“07/20”) and shorten the title like this:
https://yourdomainname.com/blog/get-your-budget-under-control-in-30-days/
It’s still a few characters too long, but that’s a significant improvement.
Other ways to make your URLs easy for Google to scan and visitors to remember is by removing nonsensical characters or strings from them. For instance:
https://yourdomainname.com/?p=123
Or something like this:
https://yourdomainname.com/utm_medium=cpc&utm_source=google&utm_campaign=best%Budget%20ToolNA&utm_adgroup=SEO%20Tool%20-%20Best&utm_term=%2Bbest%20%2Bseo%20%2Btool&gclid=Bj1UCUjosi9nT3NJWOD3ARIsNSCj_B
There’s been talk about hiding URLs like the Safari browser for Apple does, but there’s been no real release date of proof of this yet! Google has been talking on & off about this for a while.
And never use any punctuation besides the “/” and “-.” Page levels should always be separated by the “/” and words in your web pages or blog posts should always be separated by “-.”
Just be careful with this one since changing your URL structure after Google has indexed your site can hurt your existing SEO work.
There are ways to repair your URLs, but you’ll have to use 301 redirects to ensure visitors don’t end up at a dead-end if they use the old URL. These redirects also help preserve all the link juice you earned from the original URL.
You’ll want to ask Code Web to assist with this. We can apply 301 redirects for renaming as well as repairing broken links.
Tell Google About Duplicate Content
Although it’s not common to publish duplicate content on a website (or to publish duplicate content from another site onto your own), there are times when it happens. Like if you publish a great blog post that another news outlet picks up and republishes.
Here’s the thing, though: You cannot rank equally for duplicate content.
So, let’s say you have this page:
https://yourdomainname.com/blog/10-best-ways-to-make-6-figures/
A well-known publication picks it up and publishes it on their site. You’re given credit for the content, but it’s still entirely duplicated content.
What you have to do then is add a canonical tag to your post so that Google knows that yours is the original and deserves to rank for searches related to making a six-figure salary.
Otherwise, Google will choose whichever URL it believes to be the source and authority on the subject and rank it in relevant searches. And you don’t want to leave that decision up to Google to make.
Google has a list of all the reasons you might have duplicate content on your site and how to use canonical tags to resolve any confusion over which page should get credit for it. Again, you’ll want your developer’s help implementing these.
Simplify Your Navigation
Like how shorter URLs make it easier for Google to decipher what each page is about, a cleaner, simpler, and well-organized site architecture helps.
This is also important for the user’s experience. The more organized and logical your navigation is, the easier it’ll be for visitors to experience everything your site has to offer without getting lost, confused or discombobulated. Again, if you create a website people want to spend more time on, the better it’ll perform in search results.
Here are some things you’ll want to do when planning the structure of your site:
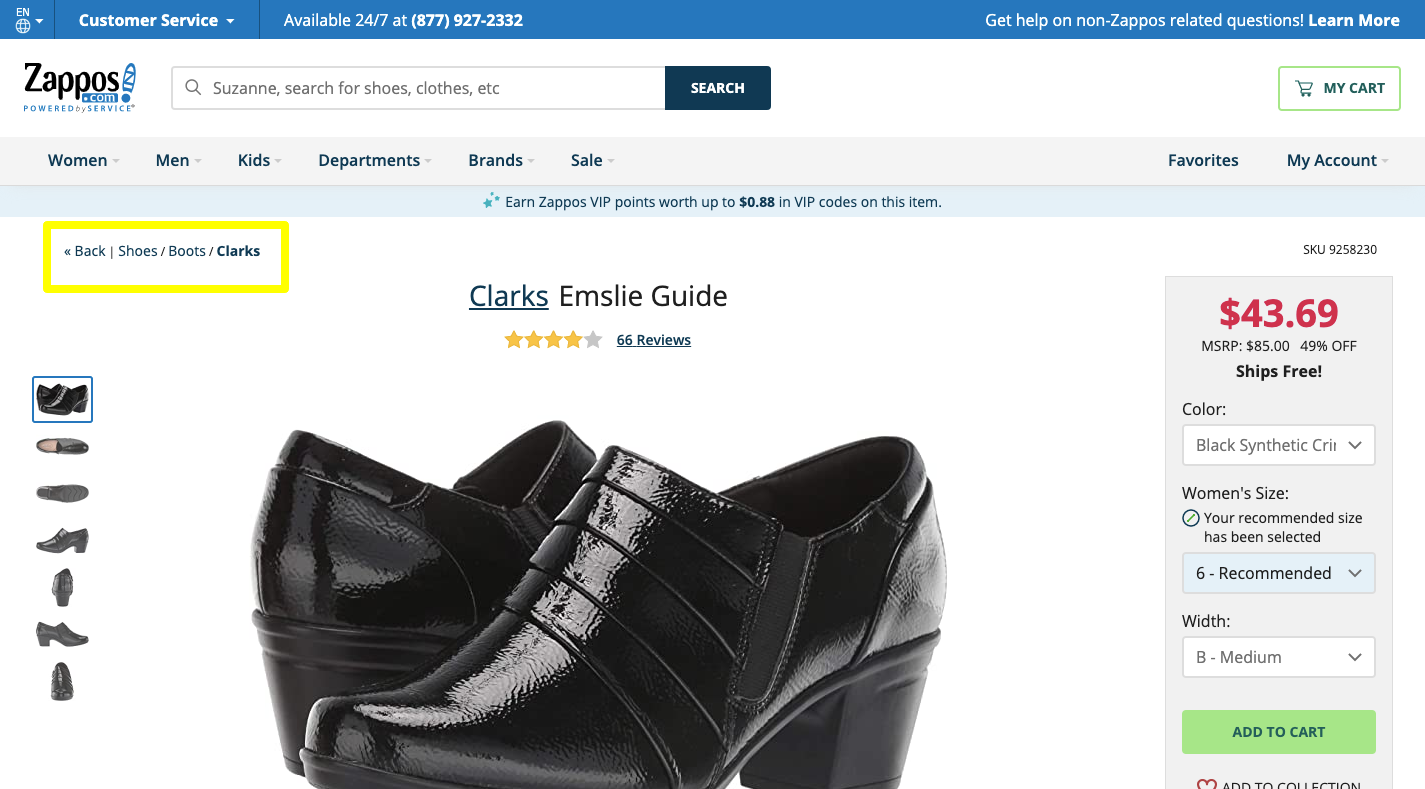
Keep page names simple, descriptive, and to the point and order them based on popularity. Zappos is an excellent example of this. It keeps its menu super basic:
Put only the most important and useful pages of your site in the top-level menu. If you take a look at Zappos’s footer, you’ll see that there’s a ton of other content on this site besides its inventory pages:
Make sure your navigation goes no more than two or three levels deep. Zappos, for instance, is a vast store, and yet it only displays one additional level of pages within its menu:
If your site needs to go more than three levels deep, use breadcrumbs to help visitors quickly backtrack and navigate the site. You can use breadcrumbs on individual content pages as well as filters and sorting on search results pages as Zappos does:
Just make sure you have a clear, direct structure that’s easy to follow, whether it’s a human or a bot trying to figure out what the site is about and what the company offers.
Fix Mobile Responsive Issues
A couple of years ago, Google gave us all a heads up about how it would change how it indexes web pages.
In the past, it would send its bots out to crawl the main version of the website, which was what visitors encountered from their desktop computers. However, because it has detected that more people are searching the web with mobile devices today than desktop, it’s changed how indexing works.
Google calls this new type of indexing mobile-first. And it will officially become the default way every website is indexed and ranked starting in early 2021.
Essentially, what this means is that Google refers to the mobile version of a website, the content on it, and how well it performs when ranking it. People prefer using their smartphones now, and it’s as simple as that 🙂
This can be problematic for anyone whose website was initially built with a desktop as the primary experience. So, the first thing you’ll want to do is make sure that the design is mobile-responsive in Google’s eyes.
Thankfully, many websites are automatically built with mobile-responsive designs thanks to website builders, page builder plugins, and design themes or templates. But it’s not a given. So, you can use two tools to check the mobile-readiness of your site:
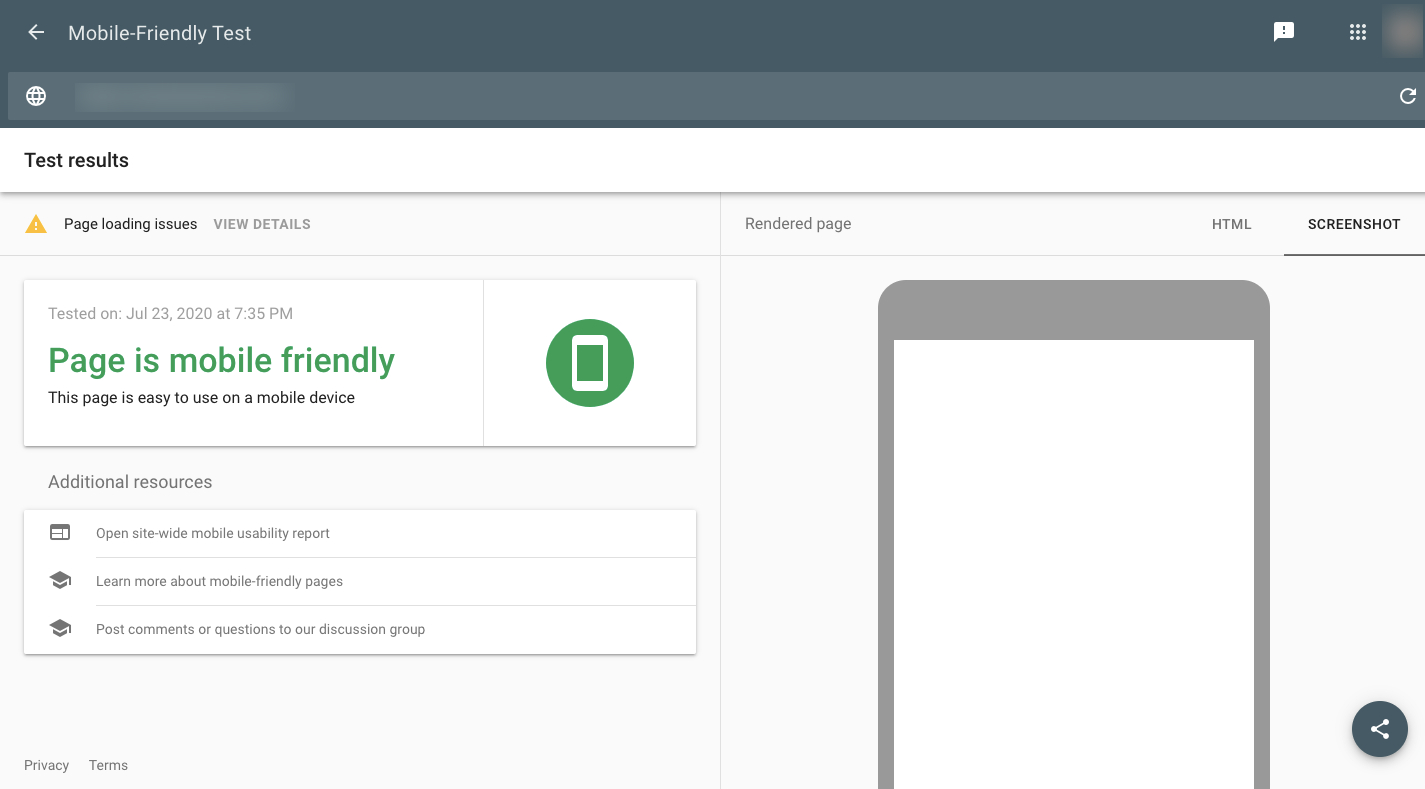
Google’s Mobile-friendly Test will let you know if your design is responsive or not:
Google will tell you if it’s mobile-friendly. It will also point you to any page loading issues (see top-left corner under “Test results”) that need to be fixed.
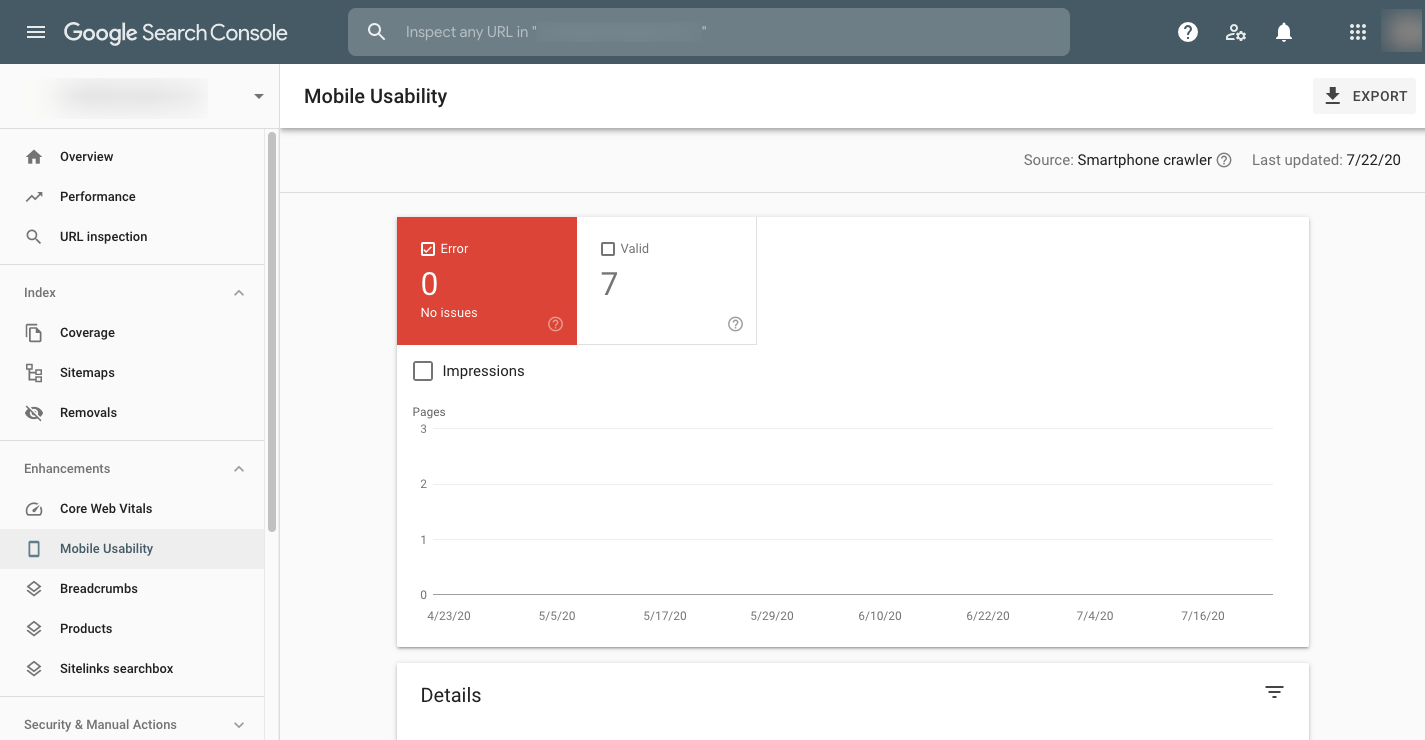
The other tool you’ll want to reference is Google Search Console. Not only is this an excellent tool for checking on your website’s performance in Google search, but Google uses this reporting tool to let website owners know about various issues with technical SEO.
To check on mobile issues, go to the “Mobile Usability” tab:
If Google finds issues in either of these tools, work with your web designer to repair them. The mobile experience is a top factor in how well your website ranks, but it’s also one of the easiest to fix.
Speed Everything Up
Your website can never be fast enough. And while this might be easy to dismiss as one of those things Google is nitpicky about, we have tons of data that show how slow speeds don’t just test visitors’ patience. A slow website will cost your business visitors, leads, and conversions.
This was something we wrote about in July, but it’s worth repeating:
The average time it takes a mobile web page to load in 27.3 seconds. This is unacceptable; your business will suffer from numbers like this 🙁
…And nearly 50% of people want a website to load in under 2 seconds. It’s not just a matter of expectation or desire, though. 40% of people will leave a website if they have to wait more than 3 seconds to see the page’s content.
Needless to say, speed optimization is going to be a critical part of your technical SEO work.
The first thing you’ll have to do is calculate how fast your mobile site loads. From your point of view, it might be quick enough, but you’ll need an impartial party to weigh in.
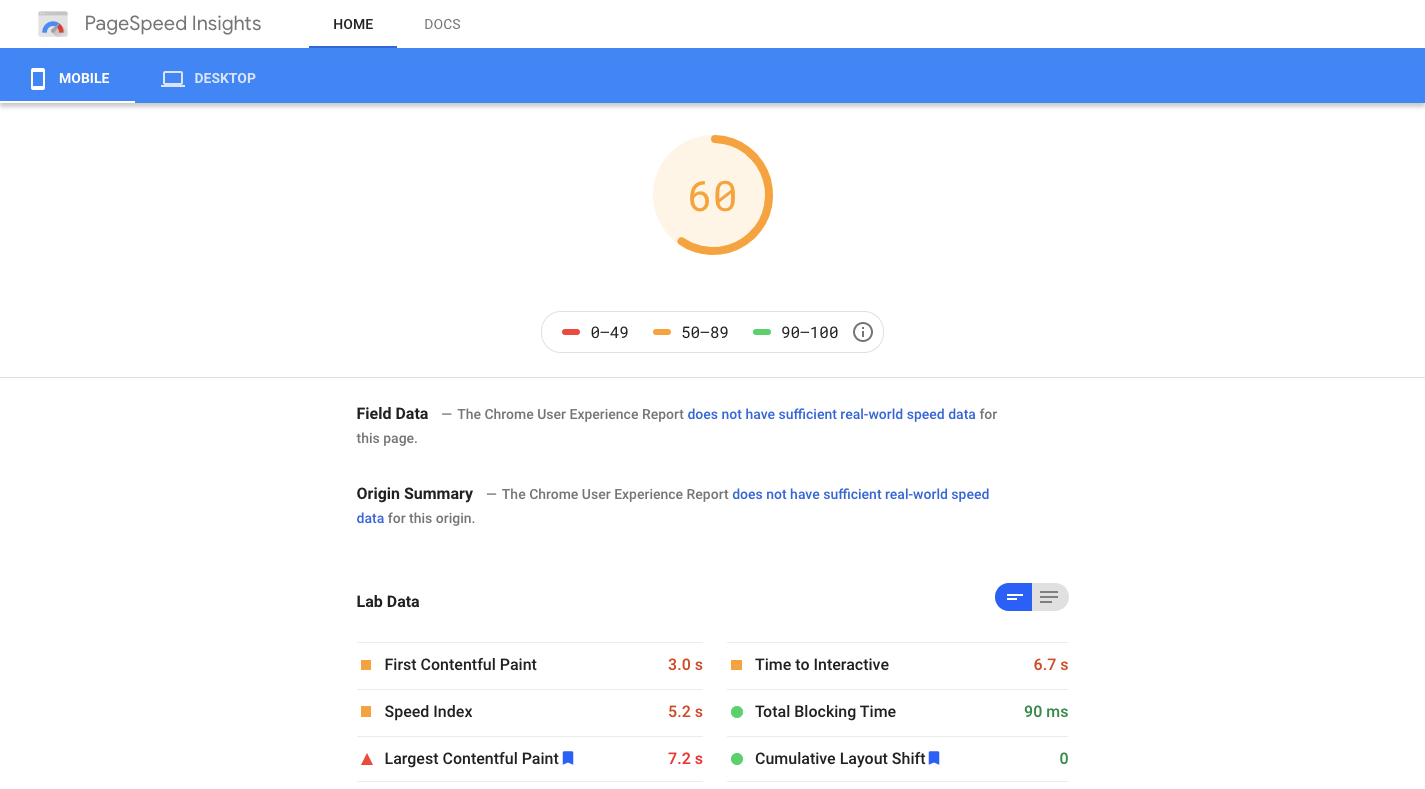
Google’s PageSpeed Insights is great for this:
If you’re not getting a green score on “Mobile,” you’ll want to work through the fixes Google provides lower on the page.
Depending on which content management system your website was built with, you might be able to apply these fixes with a caching plugin or extension quickly. This will allow you to enable speed-up features like:
- Page and browser caching
- Gzip compression
- Minification
- Combining HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code into single files
- Elimination of render-blocking JavaScript
- Elimination of unused code and assets
- Database cleanup
You’ll also want to check in on your web host again. If your host’s servers aren’t fast enough, it might be time to look for a different provider. They should be helping you with server-side caching and other optimization of resources.
Make Your Images Lighter
The performance optimizations above will do an excellent job of helping your server more easily manage your website’s code, scripts, and content. But you really shouldn’t stop there.
Images can pose a huge obstacle when it comes to optimizing a website for speed.
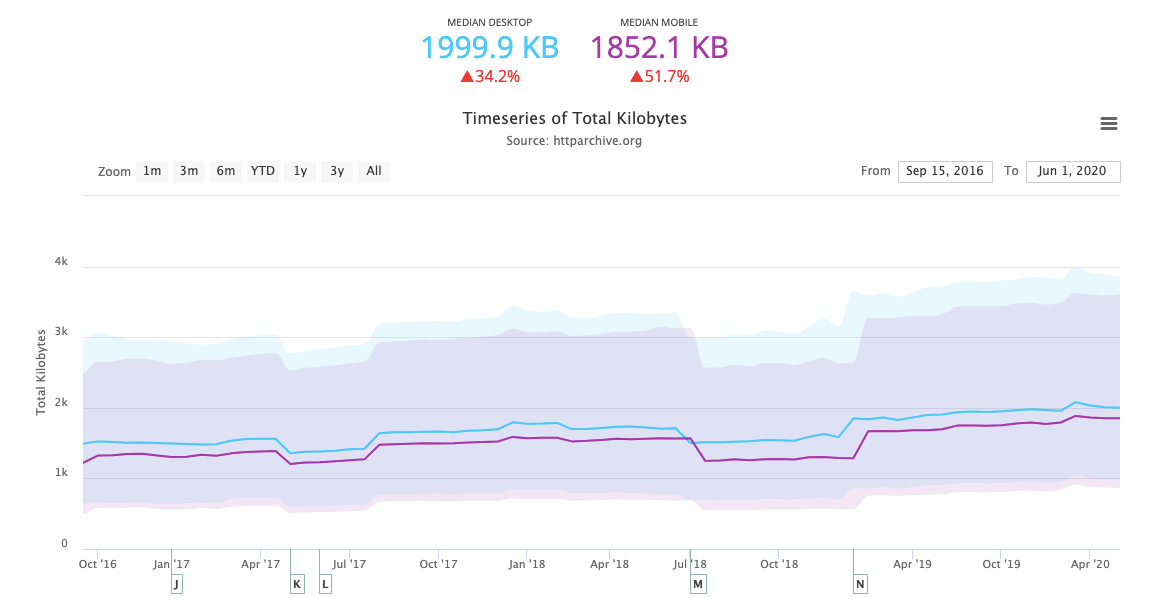
HTTP Archive keeps track of crucial technical SEO metrics across the web, like the average size of web pages and their images.
According to its most recent data, the average page size of the 5+ million websites analyzed is 1852.1 KB on mobile.
It’s a tad bit smaller than desktop (1999.9 KB), but you have to keep in mind that there’s a lot less room to display a website on mobile, which means it’ll take longer to load the same amount of assets that would appear on the desktop. So, we need to focus on shrinking down the size of each page — or, at the very least, its resources.
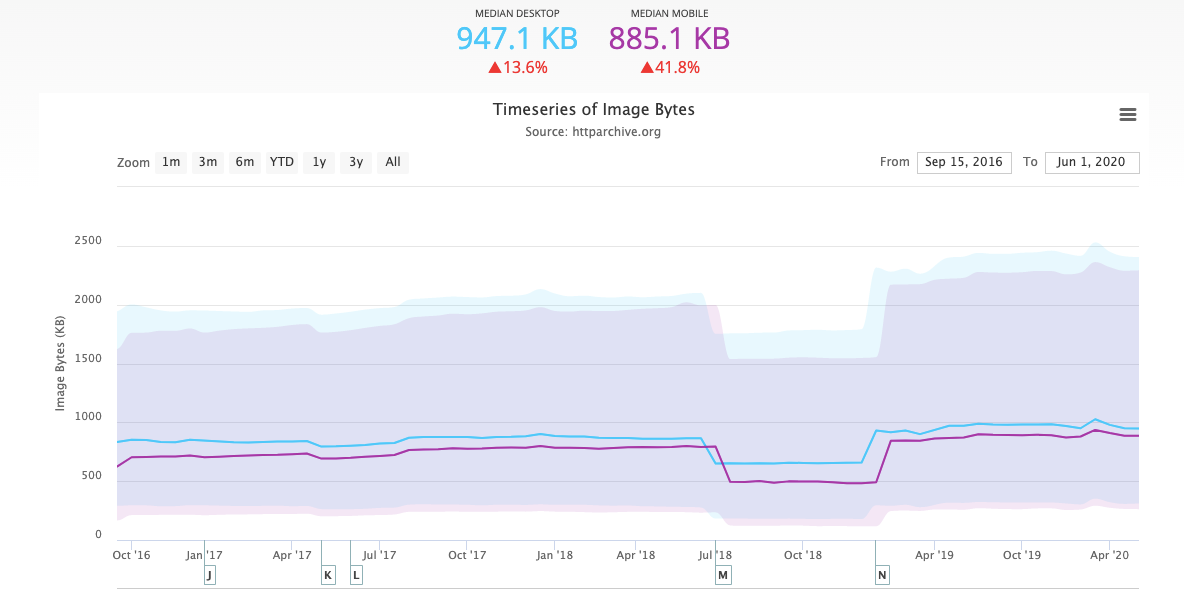
Here’s what HTTP Archive tells us about the average size of images on a web page:
Regardless of which metric we focus on — mobile or desktop — images comprise about 47% of a website’s total weight.
If you’re serious about speeding up your website to improve the visitors’ experience, then you’ll have to get those images down to a more manageable size. You can do this with a tool that resizes and compresses your images.
If you want to handle this yourself, you can use free online tools like ResizeImage.net.
You can also install an image optimization plugin or extension within your content management system. There are some great ones out there that not only make resizing and compression much easier, but they automate the process, so you don’t have to worry about it.
If you have an existing site and images, and you’re curious to see if they’re causing issues with speed, you can turn to PageSpeed Insights again for this. Google will tell you exactly which images need to be optimized.
Strengthen Your Site’s Security
Tip #2 in this checklist (“Move to HTTPS”) is an excellent first step in protecting your website from hackers. That said, you can never have enough security, especially as the hackers wise up to how we defend a website against attack.
As they get creative and persistent in their attacks, you’ll need extra protection in place.
The first thing to do is check with your web hosting company to ensure all the server and website security measures they can offer you are in place.
Server security comes in the form of things like 24/7 surveillance of their data centers, restricted card key access, locked servers, data encryption, and more. This is something you can’t and won’t handle on your own, so you must have a web host that does.
Your web host should also be able to help with things like:
- Firewalls
- SSL certificates
- Automated backups
- PHP updates
- Security monitoring
There are other website security strategies you’ll need to apply to your website.
According to the Sucuri 2019 Hacked Website Threat Research Report, the most common types of attacks on a website are SEO spam (62%), with malware reinfections (47%) a close second. But these aren’t the only things website owners should be worried about. There are also phishing scams, credit card stealers, comment spam, brute force attacks, cross-site scripting, DDoS attacks… The list goes on.
How can you possibly protect your site from all these threats? By taking a proactive and reactive approach.
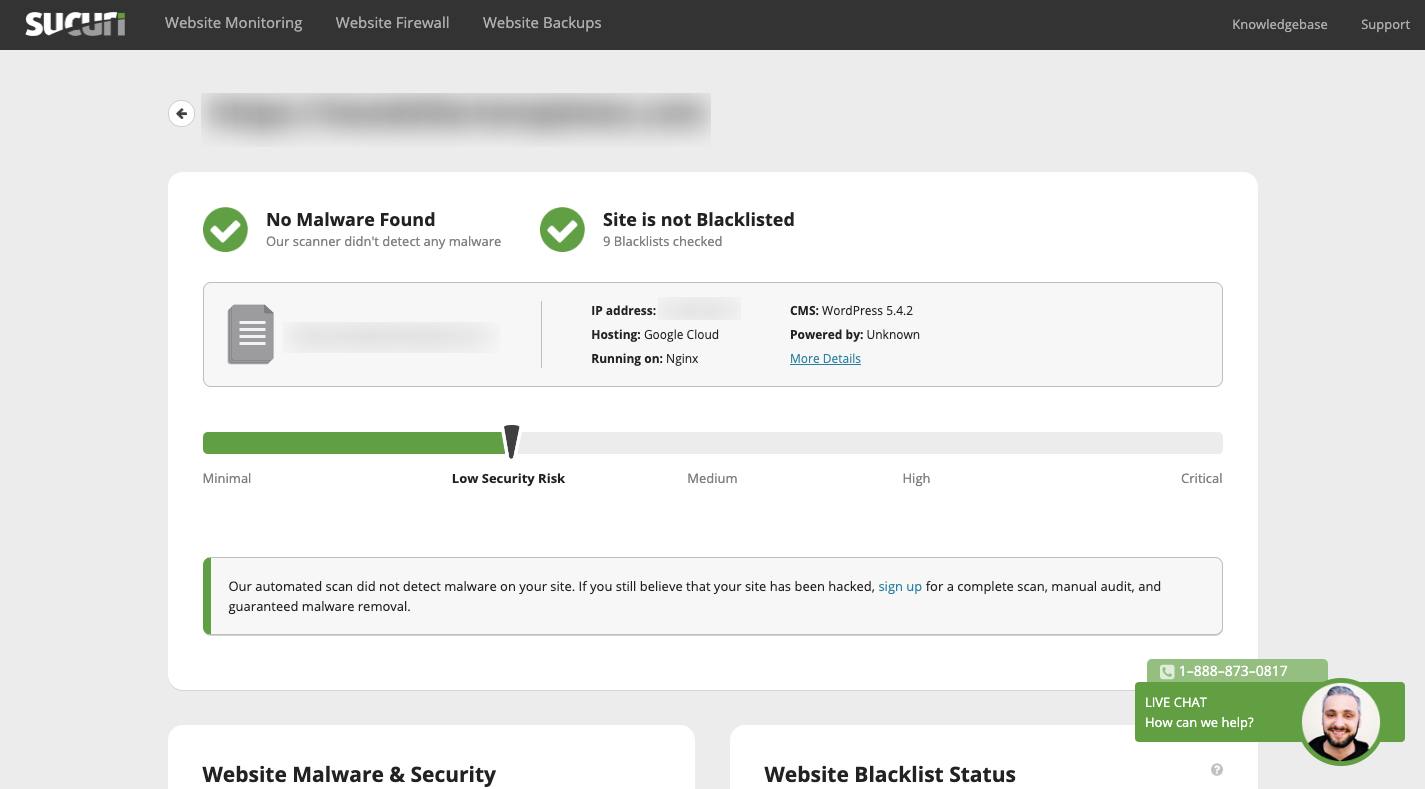
To be proactive, you’ll want to use a security scanner. Your host may be able to help with this, but it’s a good idea to use one on your own, too. Sucuri SiteCheck is a good one to start with.
This tool will:
- Scan your site for malware and other security threats.
- Let you know if you’ve been blacklisted by Google or other search engines for having an unsafe website.
- Provide suggestions on how to improve the security of your site.
You could also install a security plugin within your website that comes with a built-in scanner. This two-in-one solution will take care of the proactive piece by implementing security features like:
- Security scanner
- Anti-spam protection
- Anti-malware detection and protection
- DDoS login protection
- Strong password enforcement
- And more
As far as being reactive, you’ll have to pay for assistance with this.
You’ll either need to get an upgrade through your web hosting provider, hire website maintenance and support provider, or work with your web developer on this. Either way, you’ll need a pro who knows how to monitor for attacks, sniff out vulnerabilities, and then quickly repair them.
Apply Structured Data
Everything we do in SEO serves two purposes:
- To give Google a crystal-clear picture of what each page on our site is about to rank it for relevant search queries.
- To create an impeccable visitor experience that Google, in return, rewards us for, with better search rankings.
Structured data implementation is a technical SEO strategy that anyone can use to tell Google more about their website and improve the appearance within the SERPs.
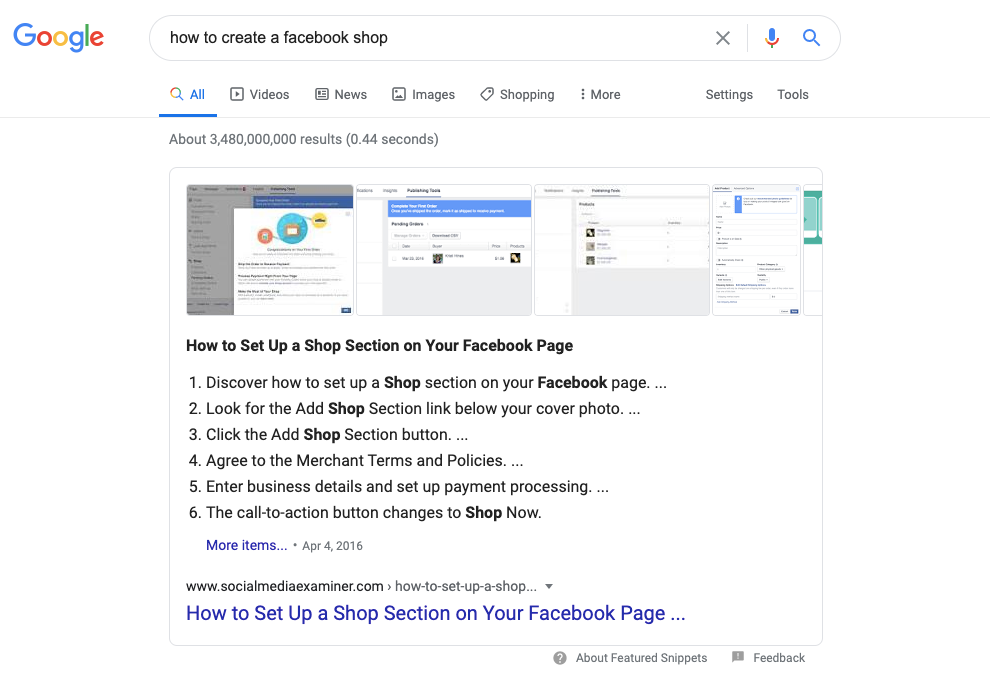
As a Google user, you’ve likely seen what can happen when a website uses structured data markup. Take, for instance, this search for “how to create a Facebook shop”:
This top result is what’s known as a featured snippet. While Google’s bots can use various signals from a page to determine if it’s worth calling out, structured data increases the chance of your page, displaying an enhanced snippet in search results.
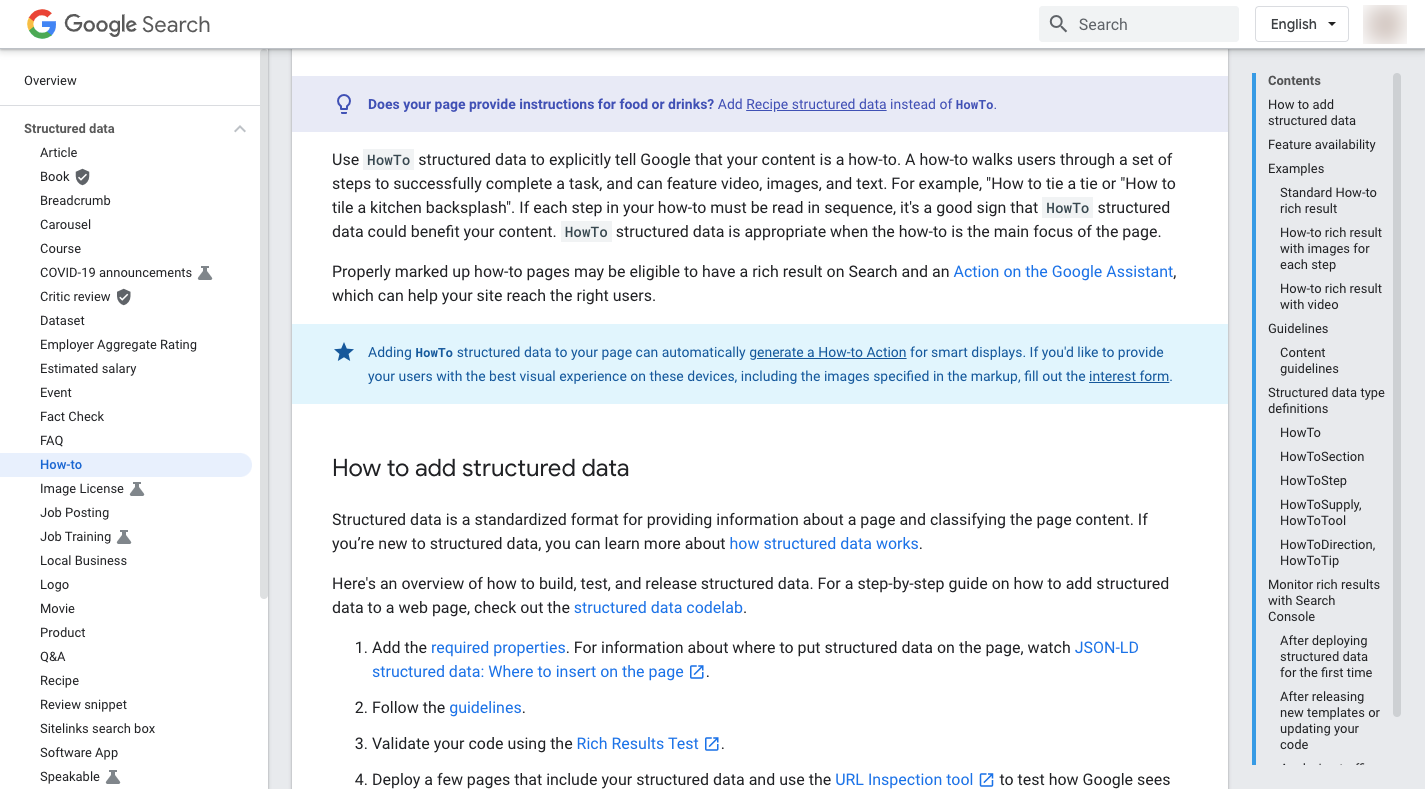
Google has a big list of all kinds of structured data you can use to improve your search results, including the “How-to” schema markup:
For instance, you can implement markup to:
- The home page with your logo and local business information.
- Blog posts with featured images and author information.
- eCommerce pages with product pricing, photos, or videos.
- Product or service review pages with average star ratings.
- And much more.
While some plugins and extensions may help you add basic markup to your pages, you’ll want Code Web’s help writing it.
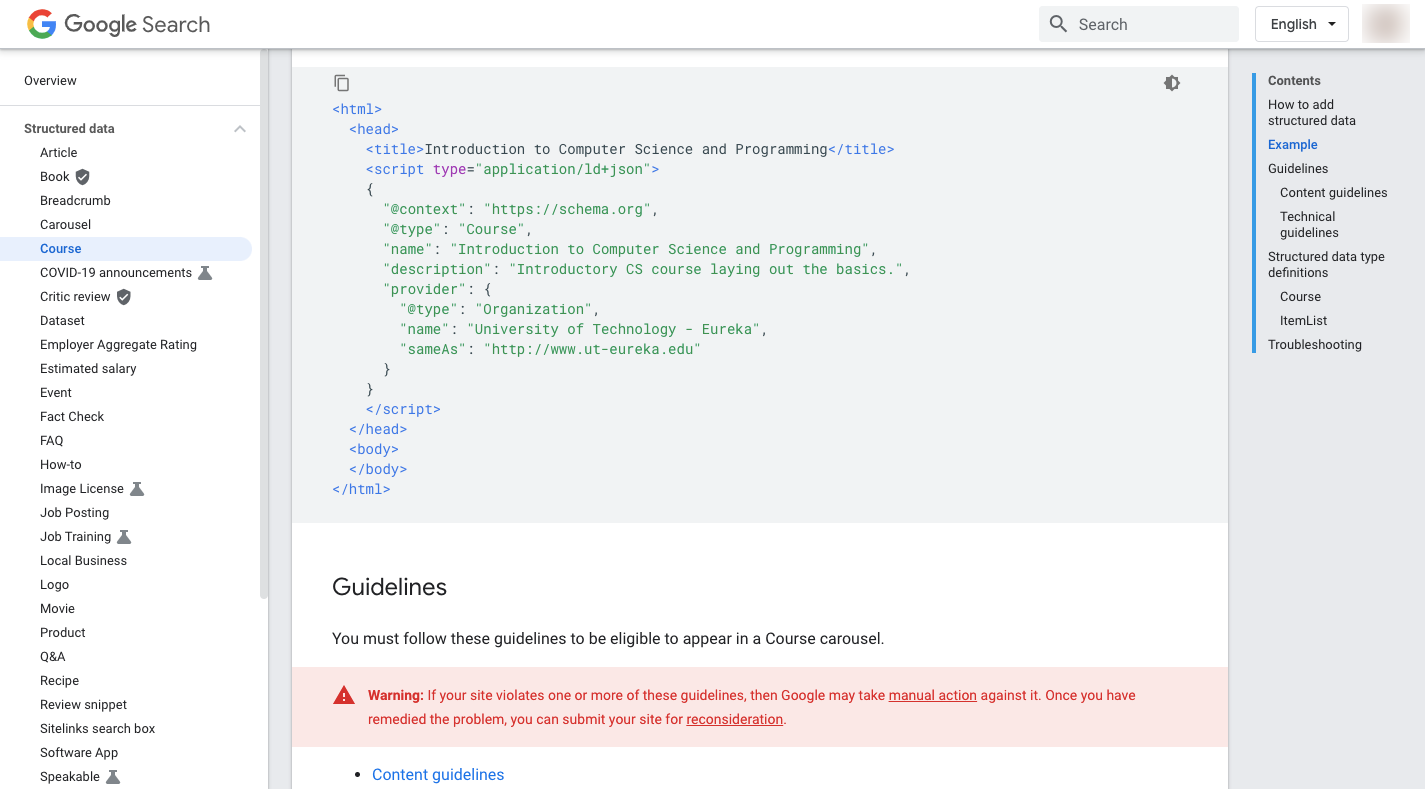
Here’s an example from Google on what the result would look like for markup attached to an online course:
If you want to give your content the best chance to shine within search engine results pages, then you need to make sure you’re taking full advantage of all that structured data has to offer. And you’ll only get that if someone can help you code this markup into each page.
Submit Your XML Sitemap to Google
The last and crucial element in your technical SEO strategy is to submit your XML sitemap to Google.
While Google will eventually discover your website on its own, there’s no guarantee it’ll know where to go to find all the pages on your site, and there’s no knowing how long it’ll take before that happens.
Submitting an XML sitemap to Google does a few things to solve this problem:
- It lets Google know the second your website is online so it can start indexing it immediately.
- It shows Google where all the pages on your site are located, so it doesn’t miss anything.
- It provides Google with an always-updated sitemap, so you don’t have to inform Google whenever you add new content to your site.
As for creating your XML sitemap, many free tools will do this for you.
If your website was built with a content management system, you could install an SEO plugin to handle it for you (the generation part, not the submission part). If you want to create the sitemap on your own, you can do that, too.
Google has a good list of XML sitemap generators that will help you find one to use.
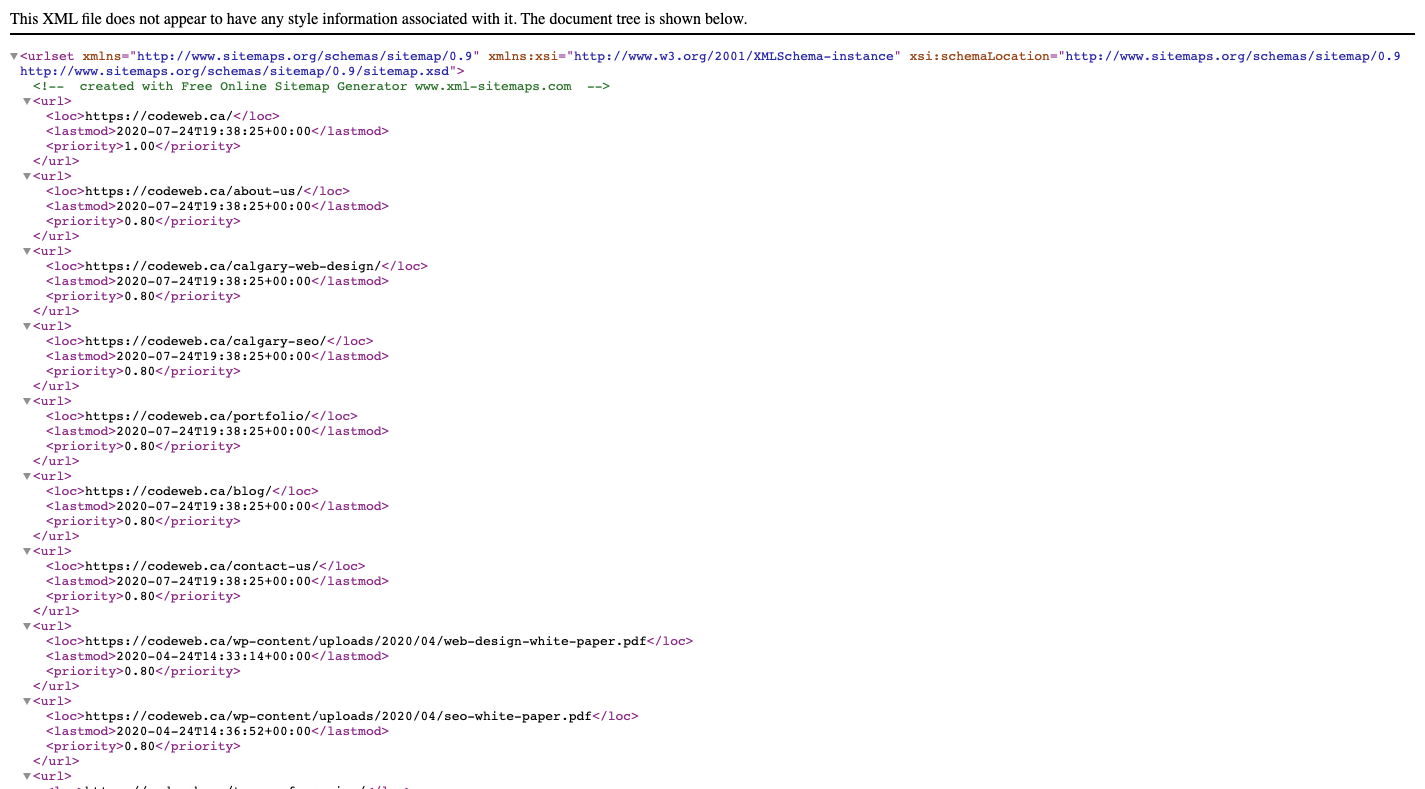
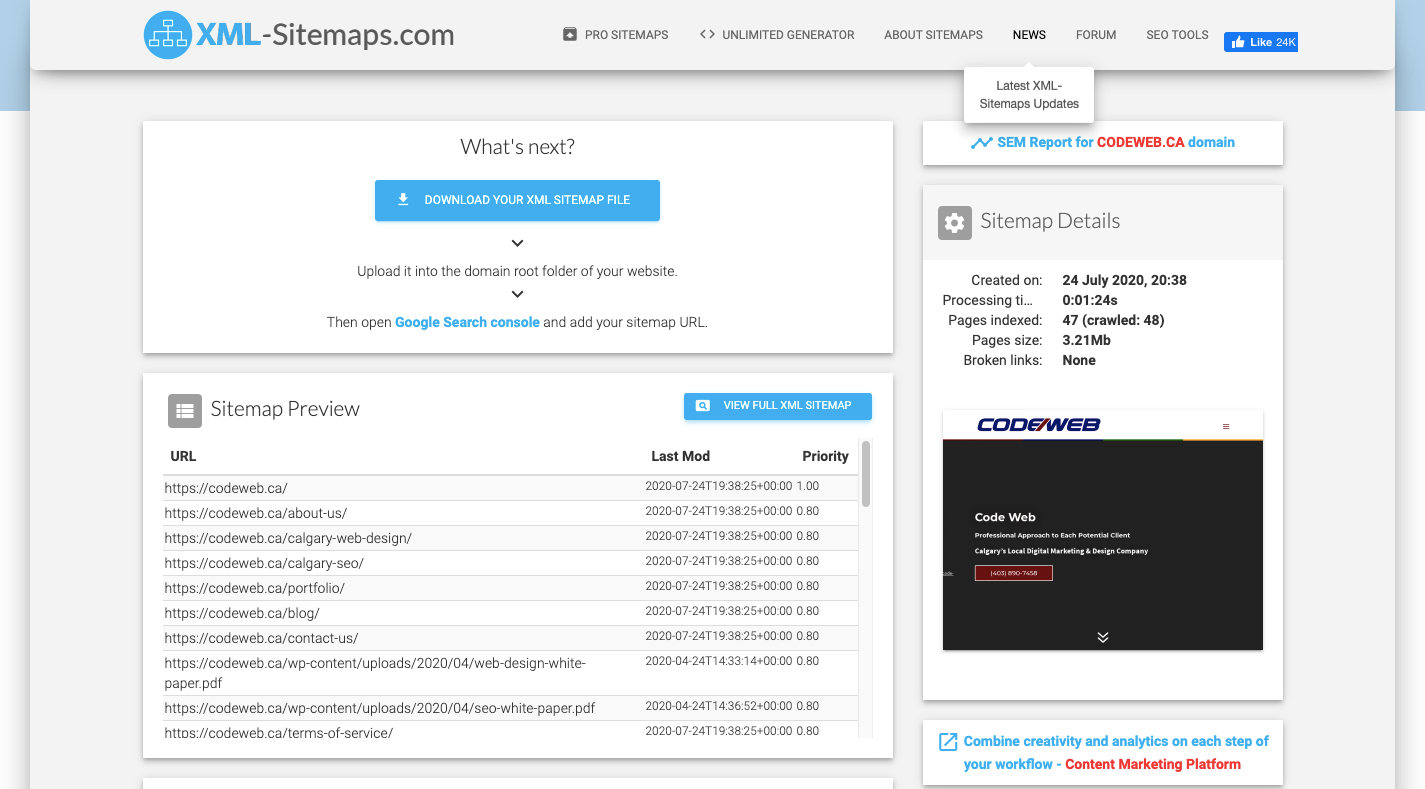
All you have to do is enter your live website URL into the generator and let it do the work. Like this one that XML-Sitemaps.com helped me create for my site:
If you manually create your sitemap this way, you’ll have to upload it to the root folder in your server so it can be indexed. (On the other hand, if you use a plugin, the sitemap URL will automatically be generated for you.)
You’ll need access to your web hosting control panel and file manager to place your downloaded file onto your server. If you need help, your web developer can assist. Just make sure the name of the file is saved as sitemap.xml.
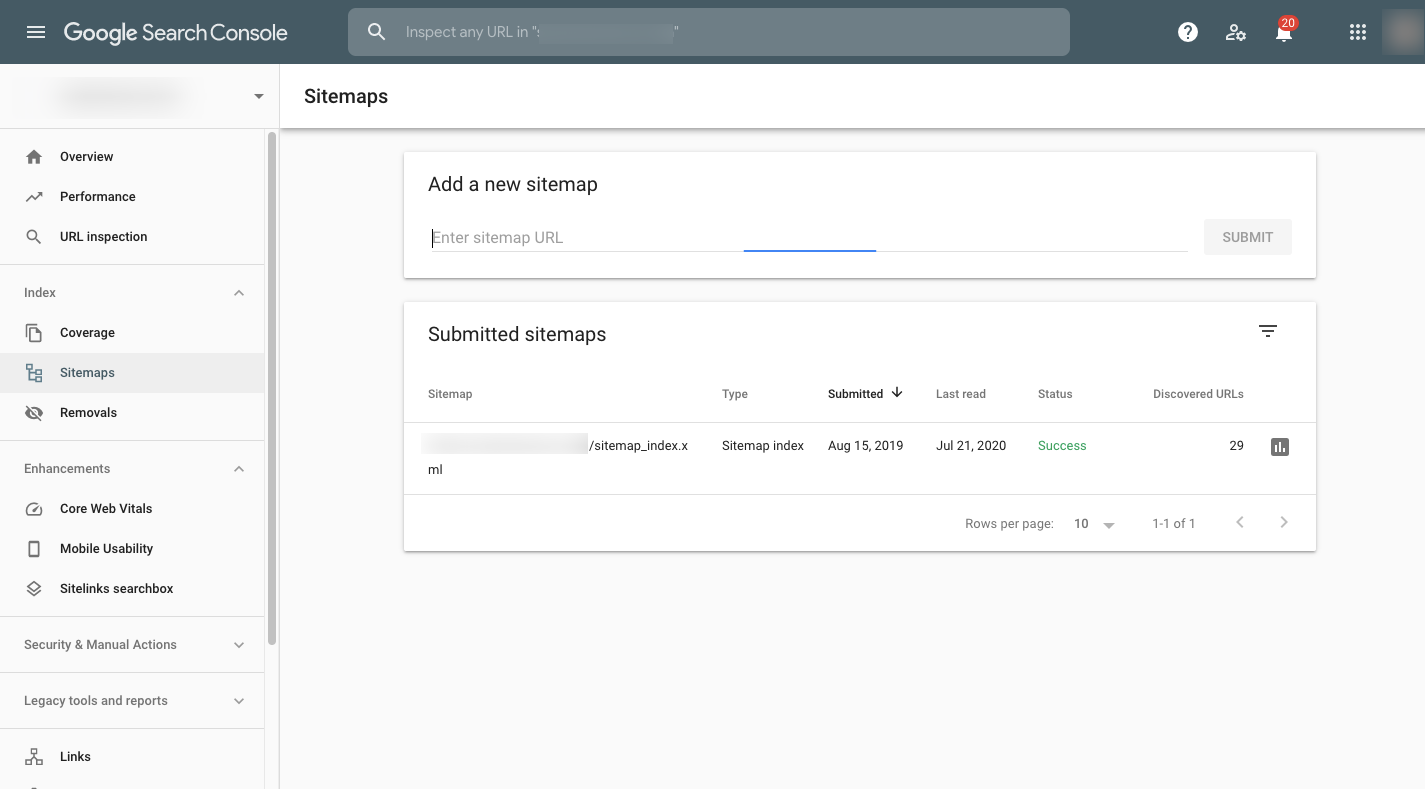
The last thing to do is submit the XML sitemap to Google. You’ll do this under the section called “Sitemaps” in Google Search Console.
Simply take the URL where your sitemap is saved (it should look like this: https://yourdomainname.com/sitemap.xml), enter it into the “Add a new sitemap” field, and Submit. Google will take it from there.
And if you’re ever worried that Google didn’t receive your request or index your site, come back to the Sitemaps page and look at the number of URLs that have been “Discovered.” You can also test it in Google Search.
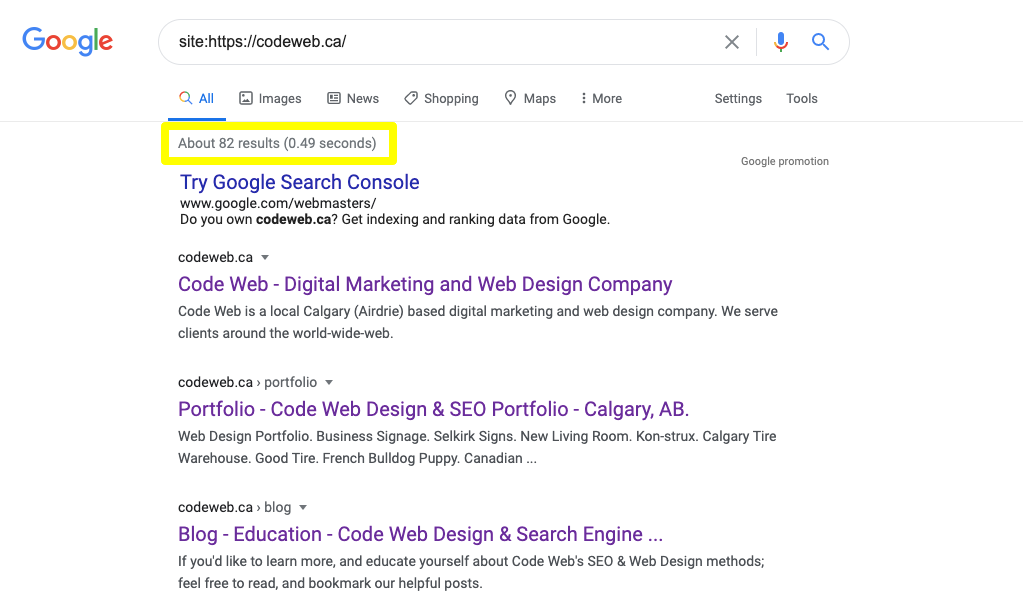
Type the following (remember to swap out “yourdomainname” for the actual name of your site) into Google or the Chrome address bar:
site:https://yourdomainname.com
Google will tell you how many pages it’s indexed and then provide you with the search listings for each. Like this:
So long as there’s no error when you upload your sitemap to Search Console, you shouldn’t have to worry about this. Google is pretty reliable when it comes to indexing the web!
Wrap-Up
Technical SEO asks us to take a good hard look at critical experience factors like speed, security, and structure. Even if your site is live and has been for a while, it’s never too late to start implementing these SEO strategies either. Google is continuously indexing and reindexing the web pages, so any improvements you make to your site will be noted.
As I’ve mentioned several times throughout this post, it would be beneficial for you to loop your web designer or developer into your technical SEO plans. They’re going to be in the best position to assess your site’s state and implement the changes needed to improve its performance.
If you do need assistance with this, we’d love to talk to you. You can fill out this contact form and let us know what you need help with, or you can give us a call at (403) 890-7458.